What Metrics Do You Use To Drive Change
Reading fourth dimension: 11 minutes
Let'south brand a bold assumption: Every software production you regularly use is data-driven. Example? Uber, Spotify, Amazon, Facebook, Netflix, the AltexSoft website you lot're viewing right now – just to proper name a few. To deliver the near value, encourage your return and loyalty, executives of companies like to start their weeks by looking at metrics – pieces of quantifiable information that illustrate the changes in revenue and customer behavior.
Of form, knowing these changes exist won't solve anything. Netflix's ex VP/CPO Gibson Biddle, explained that they used data to hypothesize then A/B test assumptions to find out what worked. That'south exactly how Netflix decided to replace their 5-star rating system with simple like and dislike buttons, innovate the "percentage friction match" of the movies, and majorly simplified the UI.
In this article, we will innovate y'all to metrics and KPIs to rail your product success. While they will give you the cognition, the real power lies in how you learn from them, how you interpret, hypothesize, and spark alter.
If you lot're new to product management, you may spend some time with our YouTube video to larn more about this practice and then go back to the commodity:
KPIs and metrics for production management
Metrics is a quantifiable measure that permit businesses to define and track the success of a product or a business activity. Metrics are used by stakeholders, marketers, and the product direction team to detect problems, prepare goals, and make informed decisions. These problems tin can relate both to engineering efforts that nosotros covered in the article on Agile development metrics and to the results of the last product.
Today, the biggest issue with metrics is non how to measure them – Google Analytics lone is a valuable tool for computing and visualizing your success. It's choosing a few central metrics to keep an eye on, spend less time tracking, and more time interim upon the found data.
Depending on what your objective is – attracting a new customer segment, improving popularity with users, getting ideas for new features – you need to cull the right metrics. KPIs are amongst primal points in building a product roadmap – they let product managers to evaluate engagement, feature usage, user experience, and, of course, commercial success.
First of all, pay attention to KPIs that contribute to your goals. Check likewise our video on production metrics:
Product management metrics explained in 12 minutes
Let's beginning with the most significant area and acquire how to measure revenue.
Metrics to forecast business success of a product
Let's face it: Stakeholders intendance the most about financial metrics. And rightfully and then. These are the numbers showing how much you're making today and will be making in the future, and subsequently – how much more y'all tin can develop or simply for how long you tin stay afloat. Stakeholders intendance well-nigh the revenue, client acquisition price (CAC) and client lifetime value (LTV or CLTV). These indicators define the fate of the company and the product.
Monthly recurring revenue (MRR)
These metrics measure out a product's full acquirement in one month. To summate them, consider the MRR at the commencement of the month, add gained revenue from new subscriptions, and decrease churned revenue from lost customers.
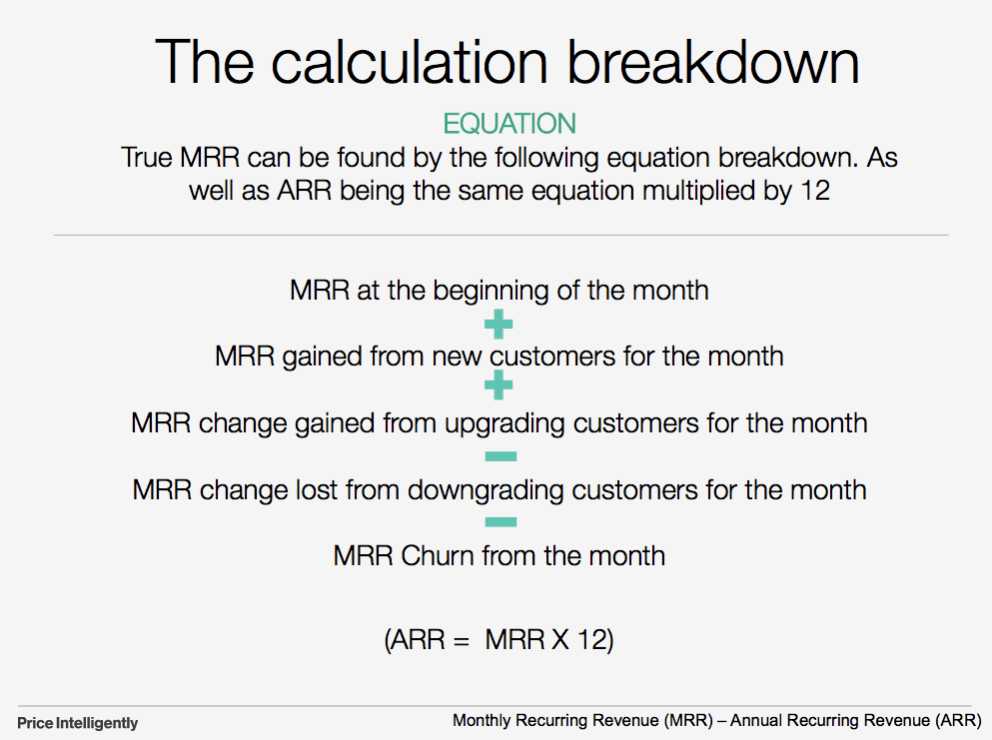
MRR calculation
Source: ProfitWell
Average acquirement per user (ARPU) allows you to count the revenue generated per user monthly or annually. You demand these metrics to ascertain the future service revenue, in case you lot're going to change the pricing programme or roll out a promotion.
There are ii types of ARPU: per new account and per existing account. ARPU per new account refers to metrics based on new accounts appearing later on the subscription programme or product cost was inverse. ARPU per existing account involves the information from accounts established before the cost alter. This is the ARPU formula:
Monthly recurring revenue / full number of accounts = ARPU
Use ARPU to compare yourself to competitors, consider different acquisition channels, or segment which tier of customers brings more than value.
How to utilise MRR and ARPU. It's an effective KPI to use to monitor a company's current health and information technology'due south peculiarly valuable in SaaS businesses working on a subscription basis. Since you don't demand to worry about one-off sales after acquiring a recurring customer, MRR is hands calculated and anticipated.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV or LTV)
These metrics allow you to calculate how much money a user volition generate in the long term. LTV displays an average profit from ane user earlier they cancel a subscription. The signal of this KPI is to bear witness you how much y'all can spend to attract a new customer at an early phase, regarding the probable profit from one person. To calculate information technology, establish an average duration of a customer lifetime (how long a customer uses a production before stopping) and average revenue per user.
Average Revenue Per User (ARPU) * Average customer lifetime = CLTV
How to use CLTV. Rails this metric to test and select client acquisition channels, purchasing cycles, and retentivity strategies.
Customer Acquisition Price (CAC)
This metric covers all the costs spent on attracting customers: marketing spendings, sales team work, advert. Sometimes these costs include salaries of marketing and sales professionals. Normally, customer acquisition price involves setting a specific period of time and full revenue. In that location are several formulas to calculate CAC, but the simplest one is:
Sales & marketing spendings for a period of fourth dimension / full # of customers generated for a period of time = CAC
How to use CAC. Use CLTV and CAC together to identify whether customers bring y'all less profit than what y'all spend on them, and whether it's time to reconsider pricing and product marketing strategy to attract more users.
Metrics to analyze and grow user engagement
Admitting less relevant to stakeholders, customer-oriented metrics volition testify yous how your product development efforts transform into user interactions. How many users notice and employ your product? How much time exercise they spend using information technology overall or a item characteristic? How do customers react to a specifically planted action or feature? As well, these metrics include data on those who stopped using a production abruptly (bounce rates).
Daily Active User/Monthly Agile User ratio
Likewise acquirement, the well-nigh valuable metrics of product growth is the number of users or subscribers for a stock-still period of fourth dimension. Simply the number of people who have subscribed or purchased your product isn't a primary KPI. What really matters is the number of active users. Metrics of this category rails how many unique visitors or users you accept per twenty-four hours (DAU), week (WAU), or month (MAU). A unique visitor is ane who visits a website at least once within a given period of time.
Daily Agile User (DAU) – the number of active users per day. An "active user" is i who signed in an account and performed some valuable activities.
Monthly Active User (MAU) – the number of agile users who complete valuable activities per calendar month.
This KPI is applied to mobile apps, online games, websites, and social networks. A unique user is defined by ID and login. In identifying the "stickiness" of a product, apply DAU/MAU ratio.
DAU/MAU = # of Daily active users / # of Monthly active users
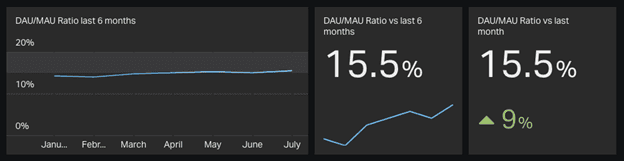
An example of DAU/MAU ratio
Source: Geckoboard
How to utilize DAU/MAU ratio. DAU/MAU of xx percent is considered a good sign, while l+ percent indicates extreme success. Growing DAU/MAU percentage allows for tracking growth or decline of a product. This ratio is used in forecasting, budgeting, or making a decision to develop new features. However, not every production must exist used daily to be considered successful. You can use Uber one time a calendar week on a Friday night out or log into Airbnb twice a year. And so, high-recency products are more prone to going viral.
Session duration
This KPI is the easiest way to track digital production usage. The best way to measure it is to take the full time users spend in your product, carve up it by a number of users, and take the mean value. Google Analytics calculates this number for y'all.
How to use the session duration metric. If you calculate the session duration of a group of bounced or churned users, you may find a clue on how to ameliorate user interaction and sympathize what made them stop using a product.
Traffic (paid/organic)
This KPI generally applies to websites, while for applications and software we use the number of users. It shows the general number of people who establish and visited the website. While organic traffic is related to the number of visitors who found a webpage via search, paid traffic counts those who visited it from paid sources, for example, paid search, social media ads, or sponsored content.
How to apply traffic metric. Paid traffic allows you to find out whether you should continue the promotion and how correct your targeting is. Traffic metrics also allows the production manager to understand which blazon of marketing is more effective.
Bounciness rate
Some other metric is the bounciness charge per unit. It allows for measuring the percentage of users who visited only i page of a website or app and left.
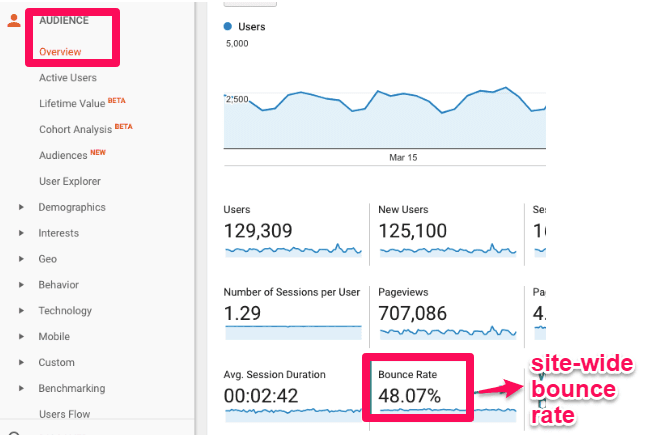
Bounce rate in Google Analytics
Source: Neil Patel
How to utilise bounce rate. Bounciness rate allows you lot to track the user behavior and empathise how to optimize your product to reduce this number and increase user attention. The next section focuses on more KPIs for alluring the users.
Metrics to go on users interested
Retentivity metrics aid understand whether your marketing and customer support efforts pay off. If y'all know your Customer Acquisition Cost, y'all know how much information technology takes to concenter a new user. Your electric current clients are much more likely to endeavor a new feature, switch to a better plan, or have function in an interview for user research, and then information technology makes sense to focus on retaining them.
Retention rate
Customer retention charge per unit (CRR) is the percentage of customers who stayed with the visitor after a sure time menstruation. You can base of operations your calculations on a number of downloads or first logins to the app.
Retention rate = Customers at the finish of the calculated period – New customers / Customers at the outset of the calculated period x 100
How to use retentivity rate: Based on this KPI, you can understand if and for how long y'all'll exist able to retain new customers when your customer memory rate is growing. In instance it dropped, you can be on the watch for a new competitor or a problem in customer service. According to the Production Benchmarks Written report by Mixpanel, the boilerplate CRR for virtually software products is beneath twenty percent over 8 weeks, depending on the industry. 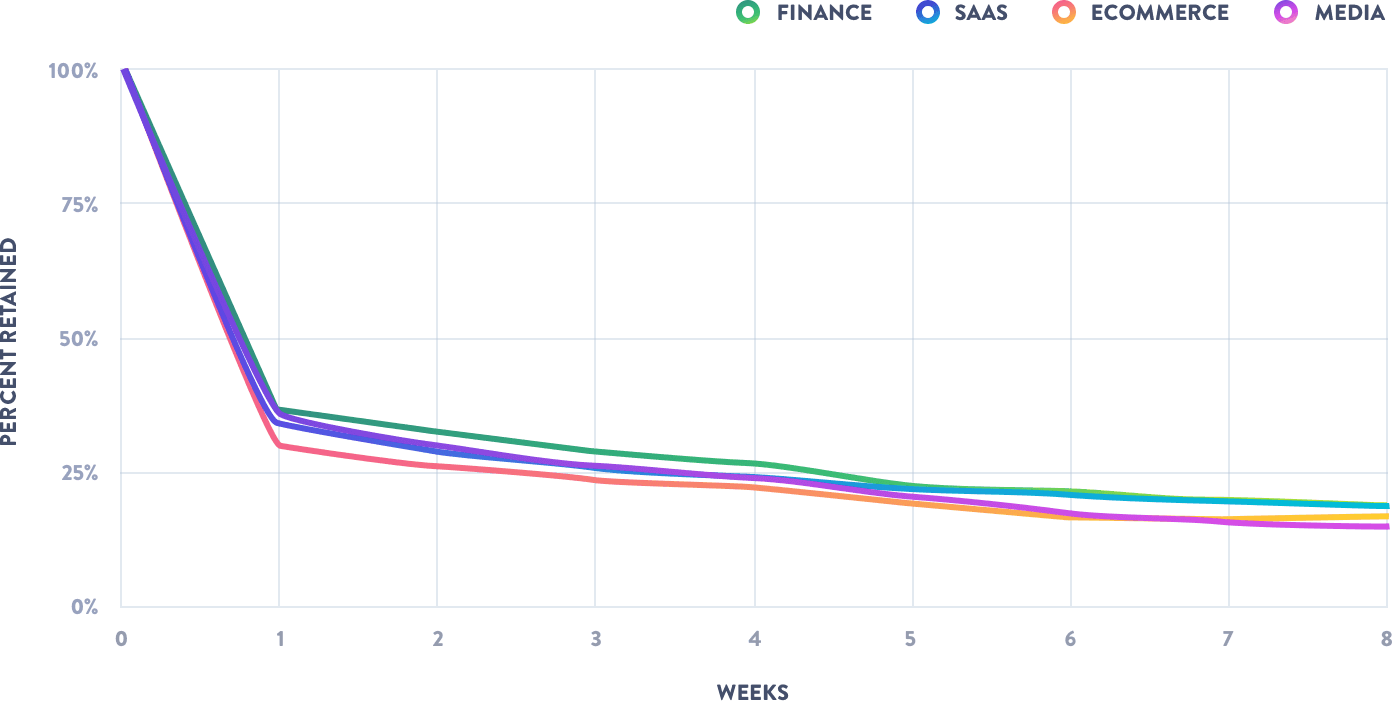
People are as likely to abandon SaaS apps as they are to bail on a media & entertainment ones after a week
Source: Product Benchmarks Report past Mixpanel
You determine what type of incoming data to use for CRR calculations: what action is considered returning and over what time period you should measure retentiveness.
Churn rate
While retention charge per unit measures the percentage of users who stayed, the churn rate measures those y'all've lost. There are two types of churn charge per unit: customer churn (number of users who canceled paid subscriptions) and revenue churn (amount of revenue lost due to customer churn). To measure customer churn rate, take the number of customers lost during a certain time catamenia and divide it by the number of customers at the beginning of this time menstruation.
Client churn rate = Customers lost / Full customers
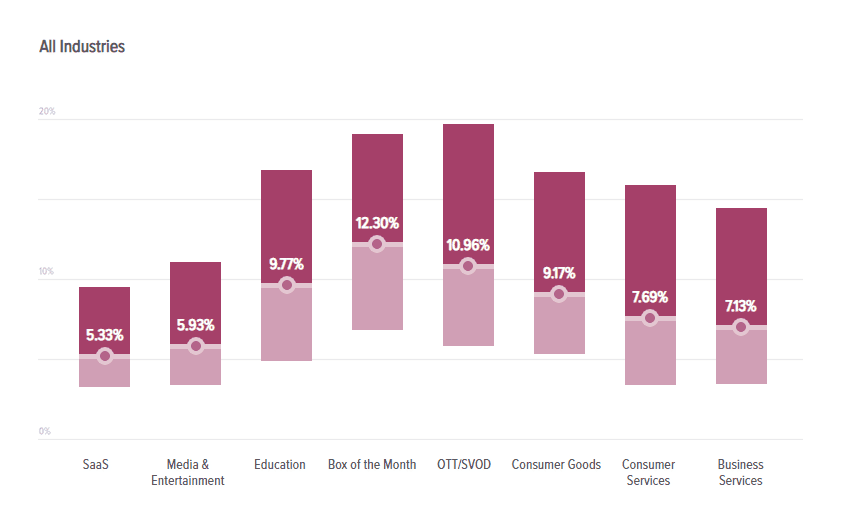
Average churn rate for subscription businesses
Source: Recurly Research
How to use churn charge per unit. In terms of concern success, it's more constructive to pay attention to revenue churn than to customer churn. Still, client churn rate can tell you a lot about customer satisfaction. If you measure out churn rate afterwards introducing a new subscription plan or applying a new feature, you can understand whether they were justified or not.
In that location also are KPIs that allows you lot to measure the popularity of new and old features and we volition discuss them at present.
Metrics to mensurate product/characteristic popularity
One of the key product manager responsibilities is to lead the product development workshop, where a product squad works on ideation of new features and UX design. To make relevant decisions, yous need convincing data on product and feature usage. Two central metrics here are the number of user actions and sessions per user.
Number of sessions per user
This metric helps understand central user beliefs: how often users come up dorsum and apply the site. It can be tracked with statistics that display the number of logins or site visits. This KPI reveals the popularity of a production – if the audience engages with it again and again. Dissimilar traffic or session duration, the number of sessions per user shows an average for a particular group of people in some time flow.
How to use number of sessions per user. Compare this information within different groups of users or visitors (retained and churned) to forecast user behavior changes earlier churn and prevent it.
Number of user actions per session
This KPI seems similar to the previous one, only it tracks not just how many times a user opened an app. It displays which actions a user fabricated and which feature(southward) they used while using the app. This metric is used to understand the popularity of a certain characteristic since it was introduced and compared to a particular period of fourth dimension. Also, you can compare these metrics of churned and retained customers and get an idea of what makes the users interested in your production.
How to use number of user deportment. Apply this information in A/B testing to make decisions about features, UX elements, and to understand customer behavior.
The last metric to consider is the level of client satisfaction and the following section is devoted to cardinal indicators that allow you lot to rails information technology.
Metrics to evaluate user satisfaction
Churn and bounce rates, traffic, and memory rate tell about customer perception of your service or product indirectly. The primary mode to learn if the customers are happy is direct customer feedback. Internet promoter score, customer satisfaction score, and customer effort are metrics that can be obtained via surveys.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
This metric measures the number of loyal customers who are probable to recommend a product (promoters), and those customers who hate it (detractors). To summate NPS, ask users to rank your production from 0 to ten. Detractors would give it from 0 to 6 points, users with 7-8 points are neutrals, and those who gave it 9-10 are promoters. The NPS formula is:
NPS = % of promoters – % of detractors
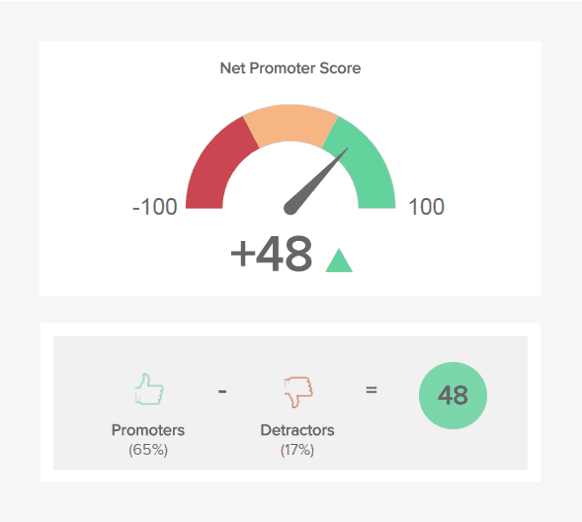
An example of NPS
Source: Datapine
Bain and Company who initially introduced the metric identified that high NPS leads to xx-threescore percent of organic growth. Same goes for negative NPS – a high number of detractors results in economic penalties.
How to utilize NPS. NPS awareness throughout the organisation motivates employees to evangelize more than value, react to issues faster, and become to the root of detractors' issues. Besides, whatever information learned well-nigh detractors should exist shared amongst all departments in a common effort to ameliorate the overall feel of your customers.
Client Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
It measures the overall level of content or discontent of a user about a specific production or service feature. Usually, users are asked to rank a product or service on a scale of 1-3, 1-5, or 1-10. Information technology'south calculated by summing the score and dividing it past the number of respondents. Unlike NPS, CSAT is directed towards evaluating satisfaction with a particular feature. Customer experience is measured with other metrics: Customer Effort Score (CES). Measured like the CSAT, you need a customer survey where users rank how easy information technology was to find a necessary information about a product.
How to use the CSAT. Ask for user feedback at several points through the customer journey and exercise it before another subscription renewal so you have time to introduce improvements. Also, utilize this metric equally an manufacture benchmark – the American Customer Satisfaction Index logs data from the biggest companies and compares stats with past results.
Concluding word: How to choose software KPI metrics?
Co-ordinate to State of Production Leadership 2019 survey by Pendo and Product Collective, the majority of product managers still focus on production features and feature delivery. Product goals remain their chief business, while adoption, revenue, and user retention remain a secondary or even 3rd business concern. Does it mean that product managers should go on measuring their success the aforementioned way? The survey shows that it's not a very favorable strategy for a lucrative product: the less you lot focus on customers, the less successful your product becomes compared to your competitors. Here are several recommendations:
- Choosing your main KPIs, focus on those that reverberate user needs.
- Align user, product, and business concern goals
- Focus on the average alphabetize rather than on total
- Focus on detail time periods (week, month, twenty-four hour period)
- Accentuate KPIs that impact long-term growth in revenue
Keep in heed that a product is not only nigh the software itself, information technology is virtually the value and customer satisfaction – then the virtually important metrics should be concerned with the user.
Source: https://www.altexsoft.com/blog/business/15-key-product-management-metrics-and-kpis/
Posted by: grenierundon1941.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Metrics Do You Use To Drive Change"
Post a Comment